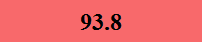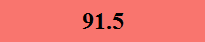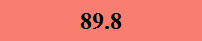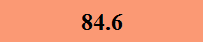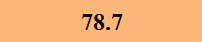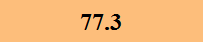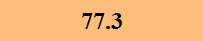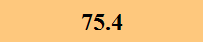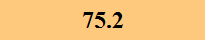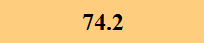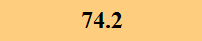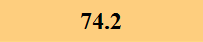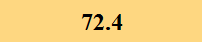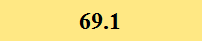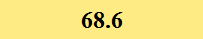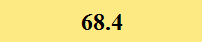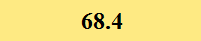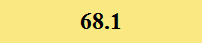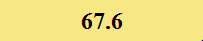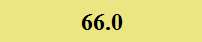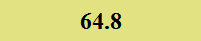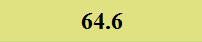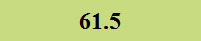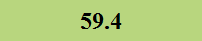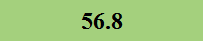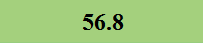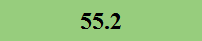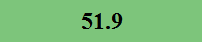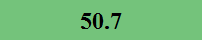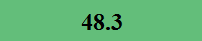Rotational Traction Values on Bermudagrass
As an athlete accelerates, stops, and changes direction, numerous forces are transmitted to the lower extremities. The interaction between an athlete's shoe and the playing surface has been indicated as a factor in lower extremity injury risk. In particular, high rotational forces may result in increased injuries to the lower extremities due to the foot becoming "entrapped" in the playing surface during pivoting movements (Torg et al., 1974).
The following list contains rotational traction values of various shoes tested on bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) grown on a sand-based rootzone and mowed at 0.75 inches. The cultivar of bermudagrass was Riviera and the turf coverage was 100%.
2019 Shoes
| Shoe | Traction (Nm) |
|---|---|
| Adidas Freak Carbon Mid | 77.0 |
| Adidas Freak Ghost | 76.8 |
| Under Armour Highlight MC | 76.5 |
| Under Armour Highlight RM | 76.1 |
| Nike Vapor Untouchable Pro 3 | 75.5 |
| Nike Alpha Menace Elite 2 | 74.6 |
| Under Armour C1N MC | 73.4 |
| Nike Force Savage 2 Shark | 72.7 |
| Nike Vapor Untouchable Varsity 3 TD | 72.3 |
| Adidas adizero 8.0 | 71.9 |
| Under Armour Nitro Low MC | 71.2 |
| Under Armour Spotlight MC | 70.8 |
2017 Shoes
| Shoe | Traction (Nm) |
|---|---|
| Nike Force Savage Elite TD | 89.6 |
| Under Armour Highlight Lux RM | 78.0 |
| Nike Alpha Menace Varsity Mid | 67.4 |
| Nike Alpha Menace Elite | 66.4 |
| Nike Vapor Speed 2 TD | 65.5 |
| Nike Vapor Untouchable Pro | 64.8 |
| Adidas Freak x Carbon Low | 63.9 |
| Under Armour Nitro Select Low MC | 63.6 |
| Adidas adiZero 5-Star 6.0 | 63.4 |
| Nike Alpha Sensory Turf | 62.9 |
| Under Armour Highlight Lux MC | 62.7 |
Previously Tested Shoes
The colors in the table below represent each shoe's traction value relative to the other shoes tested on bermudagrass, with red being the highest and green being the lowest.
*HSD: Tukey Honestly Significant Difference Test. Traction means within the value listed are not statistically different from one another.
Interpretation of Results
Rotational traction measured with mechanical devices such as Pennfoot allow for comparisons among shoe-types and playing surfaces; however, 'safe' and 'unsafe' traction levels have not been established in the scientific community, as this type of data has not been directly correlated with injury risk. Although researchers have yet to establish 'safe' threshold levels, it is generally accepted that low levels of rotational traction are desired over high levels from a lower extremity injury risk standpoint (Lambson et al., 1996). However, if traction is too low, playability may be reduced as athletes may be prone to slipping, thus increasing potential for other types of injuries.
Rotational traction values are presented in Newton-meters (Nm), which is the standard rotational traction unit (ASTM, 2009).
Traction data (four measurements per each shoe-surface combination) were analyzed for each playing surface using Analysis of Variance (ANOVA). Tukey's Honestly Significant Differences (HSD) test was used for means separation at the alpha = 0.05 level. It is important to note that traction values within the HSD value listed are not statistically different from one another.
Disclaimer: The traction values reported in this database represent the traction of each shoe under the conditions on the day of testing. Variations in traction values due to surface wetness, turf coverage, mowing height, soil type, soil moisture, soil compaction, soil temperature, air temperature, and other environmental conditions are possible. Additionally, athlete age, athlete weight, athlete skill level, and other attributes affect traction. Rotational traction values have not been directly correlated to injury risk.