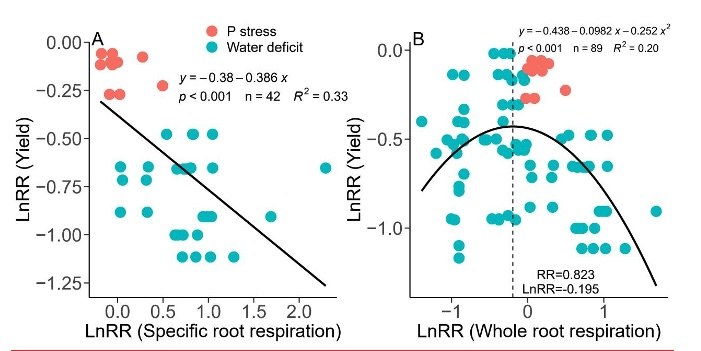
Graphs showing LnRR, specific root respiration and whole root respiration
Authors
Du, Pengzhen; Jonathan Lynch; Zhengli Sun; Feng-Min Li
Source
Plant and Soil
Download Options
from the journal (in press August 1 2024)
Abstract
Background and aims: Functional traits are fundamental for understanding and predicting crop responses to abiotic stress and yield improvement. Root functional traits are key determinants of carbon allocation and water transport efficiency. However, there are few studies integrating the effects of physiological and anatomical phenotypes in roots on yield.
Methods: We performed a global scale data analysis to quantify the ecological effects of root functional traits on yield under abiotic stress. A field study was also conducted to test the relationships between yield and root anatomical traits such as cortex area and xylem area in two semi-arid regions in China.
Key Results: The search of literature on the relationships between yield and root phenotypes was fairly consistent with the results in the field. Meta-analysis showed specific root respiration was negatively related to yield under stress. Critical thresholds of whole root respiration (RR=0.823) and xylem area (RR=0.912) were observed for better yield under stress. Hydraulic conductance was positively correlated with xylem area, stele diameter and vessel number under stress. In the field study, there were inverse relationships between yield and cortex area and xylem area was positively related to wheat yield at both sites.
Conclusions: Our study suggests that there are inverse relationships between yield and cortex area and respiration. Increased yield was associated with decreased whole root respiration with potentially smaller cortical tissue when whole respiration under stress was reduced by less than 17.7% compared with the control. However, increased xylem area contributed to high yields at both sites under rain-fed conditions.

